The ng-app Directive:
The ng-app directive is a starting point of AngularJS Application. It initializes the AngularJS framework automatically. AngularJS framework will first check for ng-app directive in a HTML document after the entire document is loaded and if ng-app is found, it bootstraps itself and compiles the HTML template.

Compiling HTML in AngularJS means attaching event listeners to the HTML to make it interactive.
Typically ng-app directives should be placed at the root of an HTML document e.g. <html> or <body> tag, so that it can control the entire DOM hierarchy. However, you can place it in any DOM element.
The AngularJS framework will only process the DOM elements and its child elements where the ng-app directive is applied. Consider the following example.
Example: ng-app placement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>ng-app Directive</title>
<script src="../Scripts/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body >
<div>
{{2/2}}
</div>
<div id="myDiv" ng-app>
{{5/2}}
<div>
{{10/2}}
</div>
</div>
<div>
{{2/2}}
</div>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, ng-app directive is placed in the div element whose id is "myDiv". Therefore, AngularJS will only compile myDiv and its child elements. It will not compile the parent or sibling elements of myDiv.
The following figure illustrates the above example.
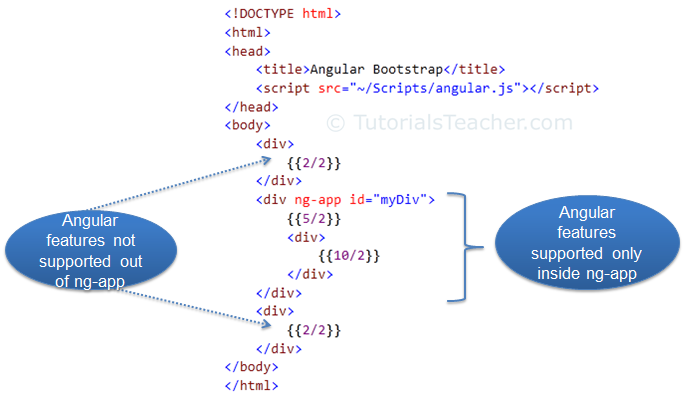 Bootstrap
Bootstrap
Note that multiple ng-app directives are NOT allowed in a single HTML document.
ng-app with Module name:
The ng-app directive can also specify an application module name. This application module separates different parts of your application such as controllers, services, filters etc.
Example: ng-app with App Module
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>ng-app Directive</title>
<script src="~/Scripts/angular.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myAngularApp">
<div>
{{2/2}}
</div>
<div>
{{5/2}}
<div>
{{10/2}}
</div>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myAngularApp', []);
</script>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, we have specified a module name using ng-app = 'myAngularApp' in the <body> tag, and then we have created 'myAngularApp' module using angular.module() function inside <script>. Visit module section to learn about Angular module in detail.
Note :
You must create a module with the same name if you have specified it with ng-app directive.
Manual Bootstrap:
We have learned that the ng-app directive auto initializes an AngularJS framework. However, we can also initialize AngularJS manually without using ng-app directive.
The following example demonstrates manual initialization of Angular.
Example: Manual Bootstrap
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html >
<head>
<title>Angular Bootstrap</title>
<script src="~/Scripts/angular.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
{{2/2}}
</div>
<div>
{{5/2}}
<div>
{{10/2}}
</div>
</div>
<script>
angular.element(document).ready(function () {
angular.bootstrap(document);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, we call angular.bootstrap() function and specify the root element, which is document object. This will initialize AngularJS and compile all the elements starting from root element i.e. the whole document in this example.
Learn about AngularJS expression in the next section.