Routing in MVC:
In the ASP.NET Web Forms application, every URL must match with a specific .aspx file. For example, a URL http://domain/studentsinfo.aspx must match with the file studentsinfo.aspx that contains code and markup for rendering a response to the browser.

Routing is not specific to MVC framework. It can be used with ASP.NET Webform application or MVC application.
ASP.NET introduced Routing to eliminate needs of mapping each URL with a physical file. Routing enable us to define URL pattern that maps to the request handler. This request handler can be a file or class. In ASP.NET Webform application, request handler is .aspx file and in MVC, it is Controller class and Action method. For example, http://domain/students can be mapped to http://domain/studentsinfo.aspx in ASP.NET Webforms and the same URL can be mapped to Student Controller and Index action method in MVC.
Route:
Route defines the URL pattern and handler information. All the configured routes of an application stored in RouteTable and will be used by Routing engine to determine appropriate handler class or file for an incoming request.
The following figure illustrates the Routing process.
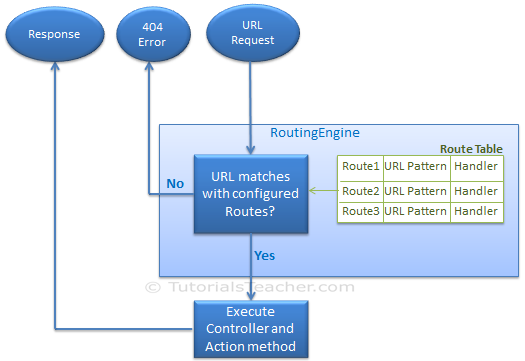 Routing in MVC
Routing in MVC
Configure Route:
Every MVC application must configure (register) at least one route, which is configured by MVC framework by default. You can register a route in RouteConfig class, which is in RouteConfig.cs under App_Start folder. The following figure illustrates how to configure a Route in the RouteConfig class .
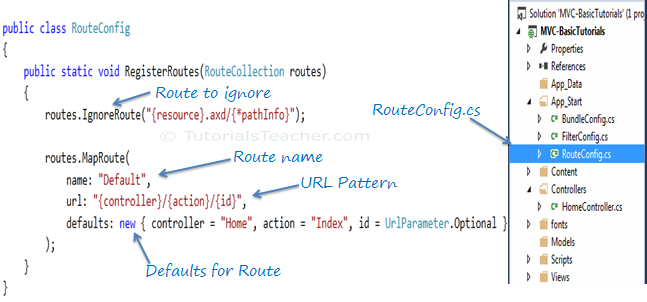 Configure Route in MVC
Configure Route in MVC
As you can see in the above figure, the route is configured using the MapRoute() extension method of RouteCollection, where name is "Default", url pattern is "{controller}/{action}/{id}" and defaults parameter for controller, action method and id parameter. Defaults specifies which controller, action method or value of id parameter should be used if they do not exist in the incoming request URL.
The same way, you can configure other routes using MapRoute method of RouteCollection. This RouteCollection is actually a property of RouteTable class.
URL Pattern:
The URL pattern is considered only after domain name part in the URL. For example, the URL pattern "{controller}/{action}/{id}" would look like localhost:1234/{controller}/{action}/{id}. Anything after "localhost:1234/" would be considered as controller name. The same way, anything after controller name would be considered as action name and then value of id parameter.
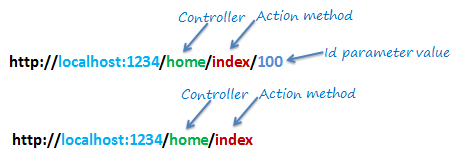 Routing in MVC
Routing in MVC
If the URL doesn't contain anything after domain name then the default controller and action method will handle the request. For example, http://lcoalhost:1234 would be handled by HomeController and Index method as configured in the defaults parameter.
The following table shows which Controller, Action method and Id parameter would handle different URLs considering above default route.
| URL
|
Controller
|
Action
|
Id
|
| http://localhost/home
|
HomeController
|
Index
|
null
|
| http://localhost/home/index/123
|
HomeController
|
Index
|
123
|
| http://localhost/home/about
|
HomeController
|
About
|
null
|
| http://localhost/home/contact
|
HomeController
|
Contact
|
null
|
| http://localhost/student
|
StudentController
|
Index
|
null
|
| http://localhost/student/edit/123
|
StudentController
|
Edit
|
123
|
Multiple Routes:
You can also configure a custom route using MapRoute extension method. You need to provide at least two parameters in MapRoute, route name and url pattern. The Defaults parameter is optional.
You can register multiple custom routes with different names. Consider the following example where we register "Student" route.
Example: Custom Routes
public class RouteConfig
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Student",
url: "students/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Student", action = "Index"}
);
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
As shown in the above code, URL pattern for the Student route is students/{id}, which specifies that any URL that starts with domainName/students, must be handled by StudentController. Notice that we haven't specified {action} in the URL pattern because we want every URL that starts with student should always use Index action of StudentController. We have specified default controller and action to handle any URL request which starts from domainname/students.
MVC framework evaluates each route in sequence. It starts with first configured route and if incoming url doesn't satisfy the URL pattern of the route then it will evaluate second route and so on. In the above example, routing engine will evaluate Student route first and if incoming url doesn't starts with /students then only it will consider second route which is default route.
The following table shows how different URLs will be mapped to Student route:
| URL
|
Controller
|
Action
|
Id
|
| http://localhost/students/123
|
StudentController
|
Index
|
123
|
| http://localhost/students/index/123
|
StudentController
|
Index
|
123
|
| http://localhost/students?Id=123
|
StudentController
|
Index
|
123
|
Route Constraints:
You can also apply restrictions on the value of parameter by configuring route constraints. For example, the following route applies a restriction on id parameter that the value of an id must be numeric.
Example: Route Constraints
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Student",
url: "student/{id}/{name}/{standardId}",
defaults: new { controller = "Student", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional, name = UrlParameter.Optional, standardId = UrlParameter.Optional },
constraints: new { id = @"\d+" }
);
So if you give non-numeric value for id parameter then that request will be handled by another route or, if there are no matching routes then "The resource could not be found" error will be thrown.
Register Routes:
Now, after configuring all the routes in RouteConfig class, you need to register it in the Application_Start() event in the Global.asax. So that it includes all your routes into RouteTable.
Example: Route Registration
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
}
}
The following figure illustrate Route registration process.
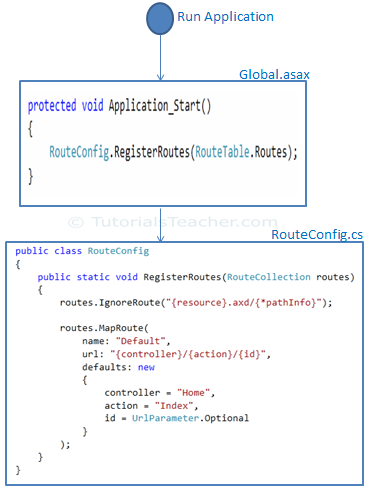 Register Route
Register Route
Thus, routing plays important role in MVC framework.
Points to Remember :
- Routing plays important role in MVC framework. Routing maps URL to physical file or class (controller class in MVC).
- Route contains URL pattern and handler information. URL pattern starts after domain name.
- Routes can be configured in RouteConfig class. Multiple custom routes can also be configured.
- Route constraints applies restrictions on the value of parameters.
- Route must be registered in Application_Start event in Global.ascx.cs file.
Learn about controller in the next section.